There’s a frustrating truth every business deals with early into its growth. To reveal that truth, I’ll start with a song title by hip-hop legend, The Notorious B.I.G.:
“Mo money, mo problems.”
The Notorious B.I.G. is literally saying “more money, more problems.” And although this hit song doesn’t dive into the intricacies of accounting, it does support a frustrating truth about business: the more revenue you generate from sales, the more you’ll have to spend to keep selling.
Let’s unpack why that’s the case with one of the most important and useful financial figures to a growing business today: variable cost.
Variable Cost Formula
Variable costs are the sum of all labor and materials required to produce a unit of your product. Your total variable cost is equal to the variable cost per unit, multiplied by the number of units produced. Your average variable cost is equal to your total variable cost, divided by the number of units produced.
Variable costs vary because they can increase and decrease as you make more or less of your product. The more units you sell, the more money you’ll make, but some of this money will need to pay for the production of more units. So, you’ll need to produce more units to actually turn a profit.
And because each unit requires a certain amount of resources, a higher number of units will raise the variable costs needed to produce them.
A kitchenware maker might sell 10 knife sets for a total of $300, for example, but maybe $100 of this revenue goes into crafting the next 10 knife sets. If the business sells 20 knife sets for $600, it pays $200 of this revenue to make the next 20. The kitchenware maker’s net revenue only increased by $100, while its variable costs rose by $300.
Hence the words of rapping sensation The Notorious B.I.G., “mo money, mo problems.”
Variable costs aren’t a “problem,” though — they’re more of a necessary evil. They play a role in several bookkeeping tasks, and both your total variable cost and average variable cost are separate calculations. With that in mind, here’s what you need to know about variable cost in fewer than 200 words:
Variable Cost Defined in 200 Words
Variable cost denotes the money your business specifically spends on the development of goods and services. Businesses can use variable costs to calculate more complex financial values, such as their contribution margin and break even point.
You can represent your variable cost two different ways: by total variable cost or by average variable cost.
Total Variable Cost
Your total variable cost is the sum of the variable cost of each individual product you’ve developed. Calculate total variable cost by multiplying the cost to make one unit of your product by the number of products you’ve developed.
For example, if it costs $60 to make one unit of your product, and you’ve made 20 units, your total variable cost is $60 x 20, or $1,200.
Average Variable Cost
Your average variable cost uses your total variable cost to determine how much, on average, it costs to produce one unit of your product. You can calculate it with the formula below (for reference, the equation to the top left of the box is your total variable cost).
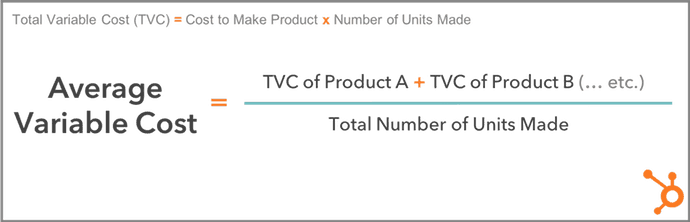
Total Variable Cost vs. Average Variable Cost
If the average variable cost of one unit is found using your total variable cost, don’t you already know how much one unit of your product costs to develop? Can’t you work backwards, and simply divide your total variable cost by the number of units you have? Not necessarily.
While total variable cost shows you how much you’re paying to develop every unit of your product, you might also have to account for products that have different variable costs per unit. That’s where average variable cost comes in.
For example, if you have 10 units of Product A at a variable cost of $60/unit, and 15 units of Product B at a variable cost of $30/unit, you have two different variable costs — $60 and $30. Your average variable cost crunches these two variable costs down to one manageable figure.
In the above example, you can find your average variable cost by adding the total variable cost of Product A ($60 x 10 units, or $600) and the total variable cost of Product B ($30 x 15 units, or $450), then dividing this sum by the total number of units produced (10 + 15, or 25).
Your average variable cost is ($600 + $450) ÷ 25, or $42 per unit.
Variable Cost Examples
So, what’s considered a variable cost to the business?
Depending on the goods or services you develop, you can classify many of your expenses as variable costs. In general, any recurring cost that doesn’t fluctuate as the business grows or shrinks is a fixed cost. A classic fixed cost is rent on office space: no matter what happens within the business, you still pay the same building rent. So, any cost that doesn’t fall into this category is likely a variable cost.
To make it easier for you to identify which of your costs you should factor into your total variable cost calculation, we’ve put together a brief list of variable cost examples below.
- Physical materials: this can include parts, cloth, and even food ingredients required to make your final product.
- Production equipment: if you automate certain parts of your product’s development, you might need to invest in more automation equipment or software as your product line gets bigger.
- Sales commissions: the more products your company sells, the more you might pay in commission to your salespeople as they win you customers.
- Staff wages: The more products you create, the more employees you might need, and the bigger your payroll.
- Credit card fees: businesses that receive credit card payments from their customers will incur higher transaction fees as they deliver more services.
- Packaging and shipping costs: you might pay to package and ship your product by the unit, and therefore more or fewer shipped units will cause these costs to vary.
It can be daunting to calculate expenses that change as your company evolves. Sometimes, you just want to know exactly what you’re paying to run your business. Using the formulas above, however, you’ll be able to easily track your variable costs no matter what stage of life your business might be in.
![]()